FCFF is a hypothetical measure of the free cash that the company would have available if it had no debt. Net cash flow refers to either the gain or loss of funds over a period (after all debts have been paid). When a business has a surplus of cash after paying all its operating costs, it is said to have a positive cash flow.
The value of your idea increases the further you take it down the development path; however, moving along that path requires the innovator’s time and efforts as well as the investor’s money. When it is desired to make a comparison between different options, then the revenue and oil price will be the same for all the alternatives. In this case, the revenue can be eliminated and the comparison between the alternatives can be made from a strictly cost point of view and the lowest cost will be the best alternative. The operating expense (OPEX) can be calculated with other expenses every year. A cash flow diagram can be used to calculate the net present value, or other economic tools can be used. The net present value is calculated using the following equation; note that it can be calculated easily using an Excel spreadsheet.
What is included in net cash flow?
These are the general types to consider and the types are different from one country to another. The cost will also vary, as it depends on the country’s laws and regulations. Operating expense (OPEX), which refers to the direct expense during operations, such as the cost of the workover or other activities, has a direct impact on the production. The indirect expenses include management salaries, computers, desks, and other usable equipment during project implementation. Where n is the project lifetime in years; D is the discount rate, which is approximately equal to the interest rate value; and NCF is the net cash flow per year. The cash flow of each activity is calculated separately first, and then the balance of the three parts is added to form NCF.

While the net cash flow formula tells you how much operating cash moves in and out for a given period of time, net income also includes all expenses. Net income subtracts both operating expenses and non-operating expenses, such as taxes, depreciation, amortization, and others. The annual return may be the gross income, net pre-tax income, net after-tax income, cash flow, or profit. ncf formula These may be calculated for one particular year or as an average over the project life. Investment may be the original total investment, depreciated book-value investment, lifetime average investment, fixed capital investment, or equity investment. The investment includes working capital and sometimes capitalized expenses such as interest on capital during construction.
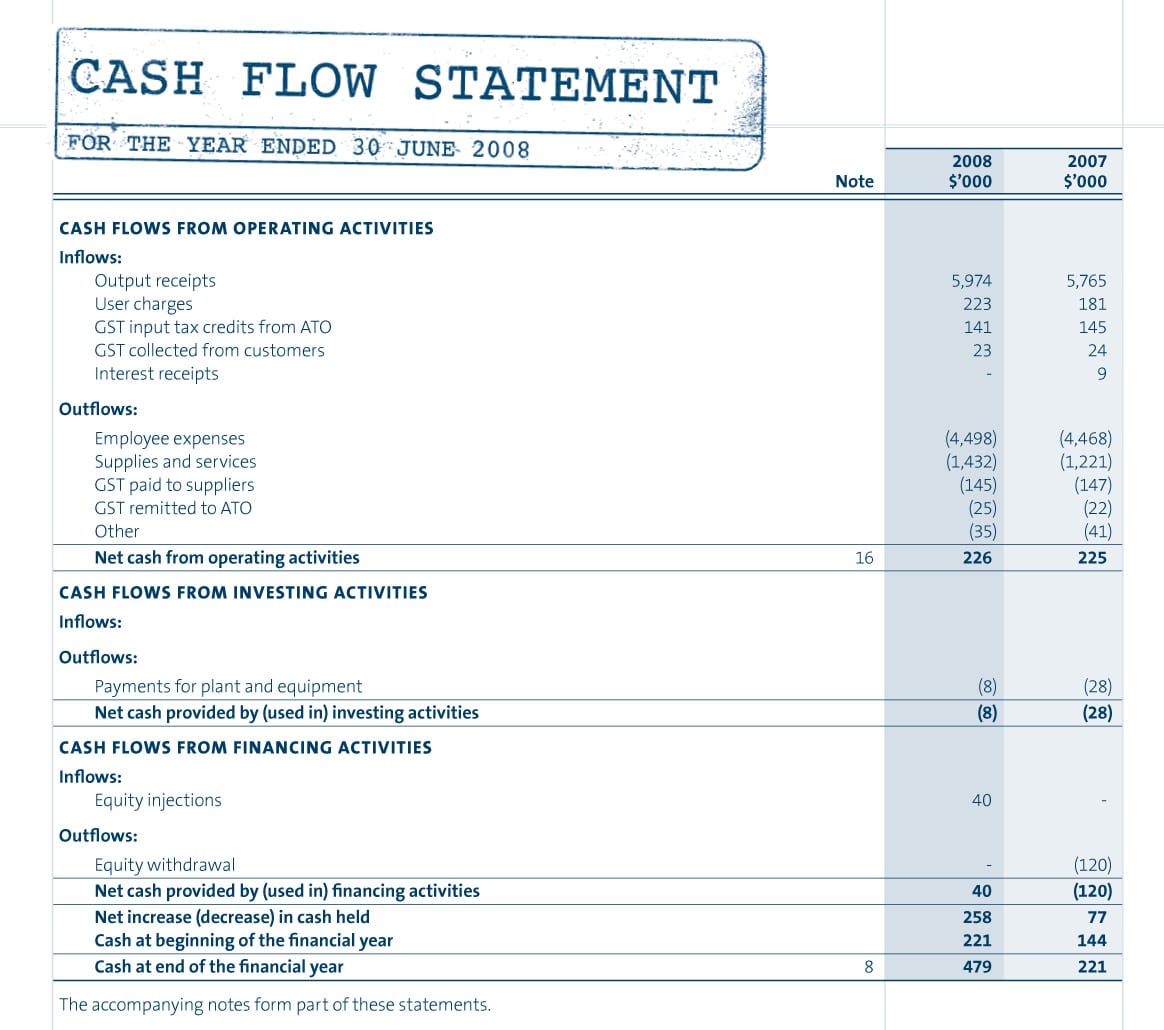
Cash Flow from Operations Calculation Example
Cash flows from investing activities include the purchase and sale of the company’s assets and funds paid for long-term investments. Another limitation of NCF is that even if a business makes a capital investment that’ll bring a substantial return on investment in the future, the NCF would still show negative for the specific time period. The most common way to calculate operating cash flow is through the indirect method, which takes into account the net income under an accrual basis of accounting. Repeated periods of positive net cash flow are a good sign that your business is ready to expand, whereas repeated periods of negative net cash flow can be a sign that your business is struggling. In order to calculate net cash, you must first add up all cash (not credit) receipts for a period. This amount is often referred to as «gross cash.» Once totaled, cash outflows paid out for obligations and liabilities are deducted from gross cash; the difference is net cash.
On the other hand, a business that generates a negative net cash flow, month after month, may be encountering financial or operational issues. Learning how to find net cash flow can be a great way to gain insight into the financial health of your business. Enter the cash flow from operations, cash flow from investing, and cash flow from financing.
How to calculate Net Cash Flow (NCF) :
Therefore, depreciation of the resource at any time is the net cash flow minus two terms. The other is the sum of the returns to the two assets (which is equal to the return on the remaining project value and consequently is unique). Net cash flow is normally calculated for uniform time intervals – quarterly or half-yearly. Similar to the current ratio, net cash is a measure of a company’s liquidity—or its ability to quickly meet its financial obligations. A company’s financial obligations can include standard operating costs, payments on debts, or investment activities.

The allocation has the properties of a rental rate applied to the accounting balance in that it is equal to the sum of interest on and depreciation of the remaining (undepreciated, present) value of the user costs of the asset. The negative of the change of the value over any period is defined to be the depreciation of the project in that period. First, the current net cash flow in the period is realized and is removed from any projection of future, remaining value.
NCF can help you identify issues with operating cash flow early so that your total cash outflows stay within your total cash inflows. Net cash flow measures the impact that changes in operating cash flow or investing activities have on your company’s finances. It provides valuable insight into expenditures and earnings, which will help you assess your operations’ overall efficiency.