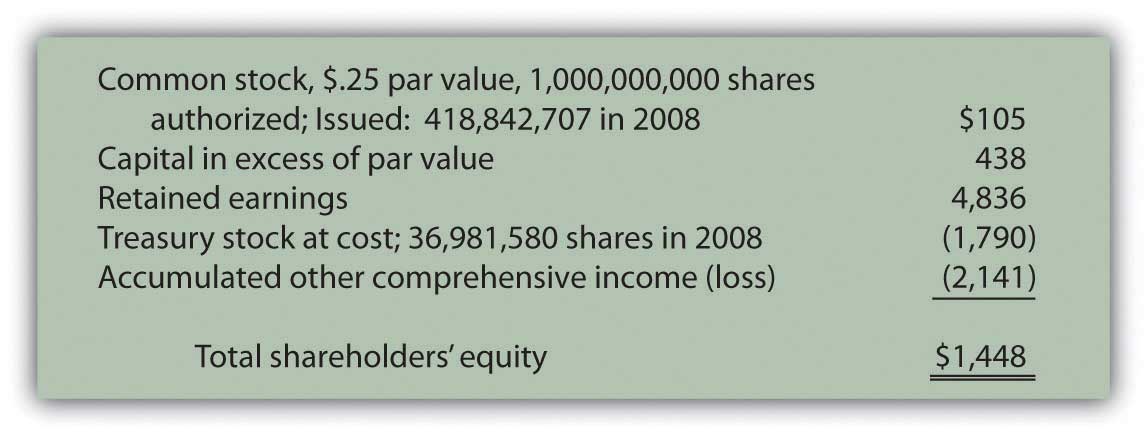
Investors contribute their share of paid-in capital as stockholders, which is the basic source of total stockholders’ equity. The amount of paid-in capital from an investor is a factor in determining his/her ownership percentage. If a share of stock has been issued and has not been reacquired by the corporation, it is said to be outstanding. Explore how corporations authorize and calculate issued shares through market cap and balance sheet methods.
Determine the Reporting Date and Period
Common stock is a type of security that represents an ownership position, or equity, in a company. When you buy a share of common stock, you are buying a part of that business. If a company was divided into 100 shares of common stock and you bought 10 shares, you would have a 10% stake in the company. If all the company’s assets were converted into cash and all its liabilities were paid off, you would receive 10% of the cash generated from the sale. However, investors generally trade common stocks rather than preferred stocks. Due to their fixed dividends and lower risk profile, preferred stocks typically have less price volatility and greater growth potential than common stocks.

Is Stockholders’ Equity Equal to Cash on Hand?
For this reason, the balance sheet should be compared with those of previous periods. Conceptually, stockholders’ equity is useful as a means of judging the funds retained within a business. If this figure is negative, it may indicate an oncoming bankruptcy for that business, particularly if there exists a large debt liability as well. First, the board of directors authorizes the company to issue a certain number of shares. The company hasn’t taken action yet; it’s just gotten approval to take action and sell some shares if it chooses to.
Thanks to the SEC, common stock outstanding is straightforward to calculate
Therefore, the value of treasury stock shares is subtracted out to arrive at total stockholders’ equity. Common stockholders have voting rights that allow them to participate in important decisions that affect the company’s future. By calculating the number of shares outstanding, the company can determine how many votes each shareholder is entitled to. As mentioned previously, operational management challenges common stock is one of the most popular forms of equity purchased on the public markets today. For many investors, the appeal of common stockholders equity lies in its relative affordability and the ease by which it can be obtained. A company receives assets such as cash when selling a product or service, or even by selling shares of its own stock or issuing bonds.
Step 3 of 3
- Both common and preferred stockholders can receive dividends from a company.
- Fear not, for we are about to demystify this process, unveiling the hidden wealth buried within financial statements.
- A balance sheet is divided into the three main accounts of assets, liabilities and stockholder’s equity.
- In order to find the amount of common stock in circulation, you can look for the common stock on balance sheet publications.
- Common stock represents ownership in a company and offers investors the potential for long-term growth.
If convertible, this fact should be indicated on the face of the balance sheet. Preferred stock is often known as a hybrid security since it generally combines the features of both equity and debt. From stockholders point of view, the negative aspect of this class of stock is that it does not possess the voting power. It means, the preferred stockholders are not entitled to vote for the election of directors and other important matters of the corporation. In addition to common stock, many corporations issue preferred stock to finance their operations. When a person buys the preferred stock of a corporation, he is known as preferred stockholder of that corporation.
This amount is recorded as common stock in the shareholder’s equity section of a balance sheet. Preferred stock is a distinct class of stock that provides different rights compared with common stock. While both types confer ownership in a company, preferred stockholders have a higher claim to the company’s assets and dividends than common stockholders. However, despite its growth potential, common stock comes with higher volatility.
Examples of liabilities include accounts payable, loans, and other debts. Confused because banks tell you that they are “crediting” your account by putting money in it? On the bank’s balance sheet, your money is a liability because the bank has to give it to you upon request. In other words, it’s your money, not the bank’s, so it’s not considered a bank asset. Depending on the company, different parties may be responsible for preparing the balance sheet. For small privately-held businesses, the balance sheet might be prepared by the owner or by a company bookkeeper.
Treasury shares can always be reissued back to stockholders for purchase when companies need to raise more capital. If a company doesn’t wish to hang on to the shares for future financing, it can choose to retire the shares. Companies may return a portion of stockholders’ equity back to stockholders when unable to adequately allocate equity capital in ways that produce desired profits. This reverse capital exchange between a company and its stockholders is known as share buybacks. Shares bought back by companies become treasury shares, and their dollar value is noted in the treasury stock contra account.
After the first year, your car would be shown on the balance sheet at the purchase price of $40,000 minus $8,000 accumulated depreciation, for a net book value of $32,000. All programs require the completion of a brief online enrollment form before payment. If you are new to HBS Online, you will be required to set up an account before enrolling in the program of your choice.
This financial statement lists everything a company owns and all of its debt. A company will be able to quickly assess whether it has borrowed too much money, whether the assets it owns are not liquid enough, or whether it has enough cash on hand to meet current demands. Preferred stock is also an equity and is the other main category of shares aside from common stock. The balance sheet is a financial statement that shows what a company owns (assets) and owes (liabilities), along with the value of the owners’ part (equity).
In short, the balance sheet is a financial statement that provides a snapshot of what a company owns and owes, as well as the amount invested by shareholders. Balance sheets can be used with other important financial statements to conduct fundamental analysis or calculate financial ratios. Because of legal requirements, the stockholders’ equity section of a corporation’s balance sheet is more expansive than the owner’s equity section of a sole proprietorship’s balance sheet.